Rigidbodies
Beginner Designer
Warning
Bullet Physics is being phased out. We no longer plan to support or expand its features as our focus shifts to Bepu Physics. We recommend transitioning to Bepu Physics for access to the latest updates and ongoing improvements.
Rigidbodies move based on physical forces applied to them, such as gravity and collisions. Typical rigidbodies are boxes, balls, furniture, and so on — objects that are pushed, pulled, and knocked around, and also have effects on other rigidbodies they collide with.
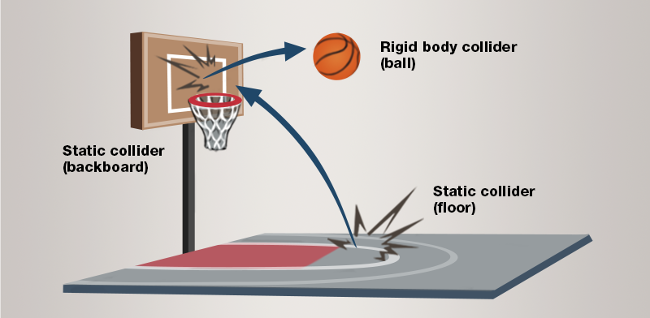
Add a rigidbody collider
Select the entity you want to be a rigidbody collider.
In the Property Grid, click Add component and select Rigidbody.

Set the collider shape to match the entity. To do this, in the Property Grid, expand the Rigidbody component to view its properties.
Next to Collider Shapes, click
 (Add) and select the shape you want.
(Add) and select the shape you want.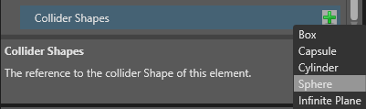
Component properties
You can adjust the rigidbody properties in the Property Grid.
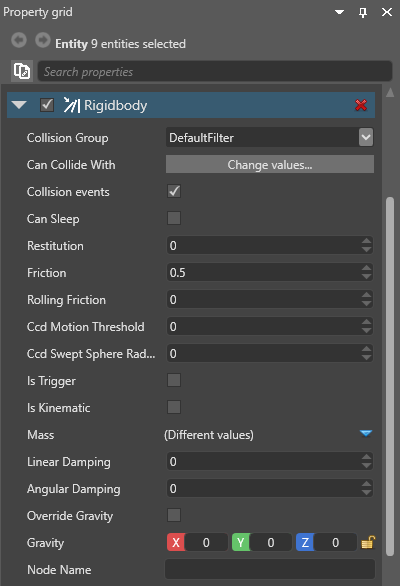
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Collision Group | Sets which collision group the object belongs to. |
| Can Collide With | Sets which groups the object collides with. |
| Collision Events | If this is enabled, the object reports collision events, which you can use in scripts. It has no effect on physics. If you have no scripts using collision events for the object, disable this option to save CPU. |
| Can Sleep | If this is enabled, the physics engine doesn't process physics objects when they're not moving. This saves CPU. |
| Restitution | Sets the amount of kinetic energy lost or gained after a collision. A typical value is between 0 and 1. If the restitution property of colliding entities is 0, the entities lose all energy and stop moving immediately on impact. If the restitution is 1, they lose no energy and rebound with the same velocity they collided at. Use this to change the "bounciness" of rigidbodies. |
| Friction | Sets the surface friction. |
| Rolling Friction | Sets the rolling friction. |
| CCD Motion Threshold | Sets the velocity at which continuous collision detection (CCD) takes over. CCD prevents fast-moving entities (such as bullets) erroneously passing through other entities. |
| CCD Swept Sphere Radius | Sets the radius of the bounding sphere containing the position between two physics frames during continuous collision detection. |
| Is Trigger | Toggles whether the rigidbody is a trigger. |
| Is Kinematic | Toggles whether the rigidbody is kinematic and therefore moved only by its Transform property. |
| Mass | Sets the collider mass. For large differences, use a point value; for example, write 0.1 or 10, not 1 or 100000. |
| Linear damping | The amount of damping for directional forces. |
| Angular damping | The amount of damping for rotational forces. |
| Override Gravity | Overrides gravity with the vector specified in Gravity. |
| Gravity | Sets a custom gravity vector applied if Override Gravity is selected. |
| Node Name | If the collider entity contains a bone structure, the node name can refer to a bones node name to be linked to that specific bone. |
| Collider Shapes | Adds a collider shape. |