Depth of field
Intermediate Artist
By default, rendering produces a very sharp image, which can look artificial. Depth of field effects simulate the behavior of a real camera lens focusing an object, leaving background and foreground objects out of focus.

To create the effect, Stride creates several versions of the original image with different intensities of blur, and interpolates between them. The more layers used, the better the quality, but at performance cost.
Properties
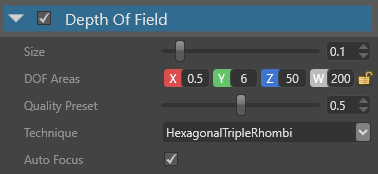
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Size | Size of the bokeh (Wikipedia), expressed as a factor of the image width so it's resolution-independent. The bigger the size, the worse the performance |
| DOF Areas | Areas of the depth of field. There are three main zones defined by their distance from the camera: near out-of-focus area (from X to Y), in-focus area (from Y to Z), and far out-of-focus area (from Z to W) |
| Technique | The technique affects both the performance and the shape of the bokeh.
|
| Auto Focus | Automatically updates the DOF areas so the camera focuses on the object at the center of the screen |
See also
- Anti-aliasing
- Fog
- Outline
- Ambient occlusion
- Bloom
- Bright filter
- Color transforms
- Lens flare
- Light streaks


